Here's a run down from the book:
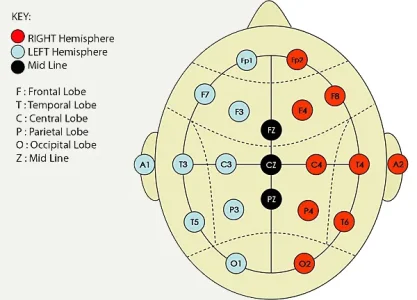
Note that A1, A2, and FZ, CZ, PZ were not used. His use of EEG has a number of inherent limitations, including not being able to sense deeper regions of the brain (where a lot of fundamental physical and emotional processing happens). His summation of the regions of the neocortex was:
Fp1 "Chief Judge"
- Provide a reason
- Decide between options
- Detect an error
Helps us decide quickly and quickly, and explain our reasoning. Helps us ignore unwanted, negative ideas and feedback.
Fp2 "Process Manager"
- Notice where you are in a task
- Perceive that you are done
- Consider a new or unpleasant idea.
Broadly, tracks whether we are at the beginning, middle, or end of a task. Helps regulate our emotions while processing negative, depressing or disruptive data.
F7 "Imaginative Mimic"
- Infer based on context
- Imagine another place or time
- Mirror others' behavior
- Ask "maybe" and "what if"
- Mentally play out a situation.
Home of the "mirror neurons." Works as a kind of mental holodeck, where we play out scenarios in an imaginative context.
F8 "Grounded Believer"
- Recall exact, literal details
- Say a word or phrase with strong emphasis
- Identity what we believe
- Rate how much we like or dislike something
- Ignore context.
Gets active when you say what's important to you in life. Helps guide our speech and recall detail about the things we consider important. Ignores context, so provides cross-contextual beliefs and details.
(Side note: autistic people show low F7 and high F8)
F3 "Deductive Analyst"
- Make logical deductions
- Backtrack or correct your thinking due to a reasoning error
- Follow a chain of reasoning
Gets active when we follow a branching logical structure or chain of reasoning towards a conclusion. Requires thinking in words or symbols. Most people who less activity here than in most regions.
F4 Expert Classifier
- Categorize a person, place, thing, event or idea.
- Have a sense for how well a concept fits a particular category.
- Links two concepts together.
Gets active when we classify and define concepts. For example, is a dolphin a fish or mammal? Like F3, underutilized by most people. Requires domain expertise to build up accurate categories.
T3 Precise Speaker
- Speak words
- Compose complex sentences
- Attend to proper grammar and word usages.
- Listen to other people's words.
This region handles words, both yours and those spoken by others. It's also used when performing tasks we've learned to do by speaking. If you talk to yourself while doing thinking (solving math problems, etc), you are likely using this region.
Some people don't use this region much, but instead may think in symbols, pictures, etc.
T4 Intuitive Listener
- Notice someone's tone of voice
- Hear when something "resonates" or "speaks to you personally
- Feel someone is speaking in a phony or false way bu cannot say why.
- Speak with powerful affect.
This region handles tone of voice and other affective qualities of sound and voice. Also home to irritation and hostility.
C3 Factual Storekeeper
- Remember a fact.
- Retrieve a memory that contains specific information such as date or time.
- Recall a sequence of action steps.
- Prepare to move your body's right side
- Skillfully draw charts, tables, and diagrams
- Attend to sensations on the right side of your body.
This region handles sensations and motor movement of the body's right side. Neurons in this regions are laid out in a way that mimics actual body layout. Activates when recalling factual "textbook" knowledge. Briefly activates when a chunk of memory is retrieved.
C4 Flowing Artist
- Remember of beautiful place.
- Retrieve a memory based on aesthetic qualities.
- Recall whole-body affect.
- Prepare to move your body's left side.
- Skillfully draw realistic, free-hand illustrations.
- Attend to sensations on the left side of your body.
The mirror image of C3 in some ways, but gets activated when we recall the most beautiful place we have ever visited. Home to fluid body motion and affect. This region is entirely nonverbal.
T5 Sensitive Mediator
- Notice other's input about your social behavior
- Are curious what someone thinks of you
- Adjust your behavior in order to appease or conform to others' expectations
- Feel embarrassed.
Like F7, this region contains "mirror neurons." When we use this region, we focus on others' judgments regarding the appropriateness of our behavior. This region actively encourages us to change out behavior by providing feelings of embarrassment and possibly shame. Can also be activated when we wonder what others are thinking of us.
T6 Purposeful Futurist
- Say the word "will"; as in what will occur in the future.
- Imagine yourself within a complex system.
- Notice abstract spatial-structural relationships.
- Assign a symbolic meaning.
- Envision your future.
This region is highly future oriented and relational. unless F7, is not "as-if" oriented, but aids in serious predictions of what will occur in reality. Holistic and weighs many abstract spatial relationships at once. Entirely nonverbal, so offerings seem obvious or mysterious. Also activated when we consider symbolic meaning.
C3 Tactical Navigator
- Identify tangible objects
- Use physical and visual cues to move your body
- Attend to where you end and the rest of the world begins
- Work a problem using rote memorization
This region is the seat of the physical sense of self in the environment. It helps us integrate visual and kinesthetic cues to guide how me move our bodies. The better this region works, the faster we integrate a multitude of visual and kinesthetic inputs in order to act with rapid precision.
P4 Strategic Gamer
- Weigh numerous pros and cons
- Calculate and compare various risks versus their likely rewards
- Objectively evaluate many factors at once
- Locate and apply leverage (influence)
This region helps us grapple highly complex programs in a comprehensive, strategic way that simultaneously considers numerous risks, uncertainties, rewards and outcomes. Helps us weigh many pros and cons at once to arrive at intuitive solutions. Associated with skillful math performance.
O1 Visual Engineer
- Read a chart or diagram
- Visually disassemble an object to visualize its components and how it works.
- Visual how elements of an object will fit together to form a structure.
- Mentally rotate an object in your mind's eye
People who rely on this region are natural engineers and architects, able to mentally rotate objects, follow charts and diagrams with ease, and project how building element will fit together in their mind's eye. This region can also compensate for or mimic deductive reasoning, by visualizing tree structures or Venn diagrams.
O2 Abstract Impressionist
- View a photograph or painting
- Sense how colors, shapes, and other elements fit aesthetically.
- Notice or set the theme of an illustration or photograph
- Gain an impression of a person's character from their appearance.
Like O1, this region is incredibly visual. Unlike O1, it is imprecise and holistic. It concerns itself with visual themes: the various inter-relationships of elements that convey an image's overall balance and meaning. We may use this region to react quickly to a person or place, detect ugly or good design, or appreciate visual art.
Summary:
Fp1 Chief Judge: Focus on explaining, making decisions, noting errors, and screening out distracting information.
Fp2 Process Manager: Focus on process, either step-by-step for tasks, or open ended creative brainstorming, or both.
F7 Imaginative Mimic: Mirror others' behavior, pick up skills by observing others, and make imaginative inferences.
F3 Deductive Analyst: Follow a chain of logical deductions and backtrack to correct thinking due to reasoning errors.
F4 Expert Classifier: Accurately place concepts by testing them against many categories at once to find a best-fit.
F8 Grounded Believer: Evaluate people and activities in terms of like or dislike, and/or recall details with high accuracy.
T3 Precise Speaker: Focus on content of the spoken word, attend to proper grammar, usage, enunciation and diction.
C3 Factual Storekeeper: Easily memorize and execute steps of movement (dance steps, etc.), and/or recall facts.
C4 Intuitive Listener: Focus on voice tone and other affective qualities of sound. Speak in a holistic way to influence.
T4 Flowing Artist: Draw, paint, dance or otherwise use your body in a flowing, spontaneous, and/or artistic manner.
T5 Sensitive Mediator: Attend to how others respond to you and later your behavior to get more desirable results.
P3 Tactical Navigator: Integrate physical space, motion, and visual clues to move skillfully through the environment.
P4 Strategic Gamer: Weigh many pros and cons, risks and uncertainties at once in order to finesse complex situations.
T6 Purposeful Futurist: State what will surely happen in the future, and/or apply a symbolic meaning to a situation.
O1 Visual Engineer: Mentally rotate, measure, arrange, assemble and explode objects with a focus on functionality.
O2 Abstract Impressionist: Notice holistic themes, patterns, and relationships in photos, paintings, and similar images.
Functions and Neocortex Activity:
Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Se types:
- Show a "tennis hop" brain pattern.
- Easily go "in the zone" in a crisis situation.
- Quickly integrate body and sensory information.
- Easily bored and need external stimulation.
- Focus on literal or common interpretations.
- Favor details that are dramatic or in motion.
The "tennis hop" brain pattern is one in which all regions of neocortex out low amplitude and out of sync. This is an effective state that requires little energy while the shifting frequencies allow the brain to quickly direct whichever regions are needed for a surprise, incoming task.
Introverted Sensing (Si)
Si types:
- Brain activity reflects their background, training, and job expertise.
- Get "in the zone" when reviewing past events.
- Tend towards rote memorization, repetition, and in-depth reviews of daily events

